Ensuring Precision in Mixing Ratios with Volumetric Ratio Mixers
Custom Color Paint Volumetric Ratio Mixer Machine Maker
In the intricate world of fluid dynamics and process control, the Volumetric Ratio Mixer stands as a critical component for industries that demand precise mixing ratios. Whether in the pharmaceutical, chemical, food and beverage, or cosmetics sectors, the ability to maintain a consistent and accurate ratio of mixed fluids is paramount. This article delves into the mechanisms and methodologies employed by Volumetric Ratio Mixers to ensure the precision of mixing ratios.
The Volumetric Ratio Mixer operates on the principle of volumetric flow control, where the flow rates of two or more fluids are precisely measured and controlled to achieve a desired mixing ratio. The accuracy of this process is contingent upon several factors, including the design of the mixer, the quality of the flow meters, and the control systems in place.
To begin with, the design of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer is tailored to the specific requirements of the application. It must accommodate the flow rates and viscosities of the fluids being mixed, as well as the physical properties that could affect the mixing process, such as density and surface tension. The mixer's geometry is engineered to facilitate laminar flow, which is essential for maintaining a consistent mixing ratio.
The heart of the Volumetric Ratio Mixer is the flow meter, which measures the volume of fluid passing through it. These meters are calibrated to ensure that they accurately reflect the volume of fluid being dispensed. The calibration process involves comparing the meter's readings to a known volume, allowing for adjustments to be made to correct any discrepancies. Regular calibration is essential to maintain the precision of the Volumetric Ratio Mixer.
Control systems play a vital role in the operation of Volumetric Ratio Mixers. These systems monitor the flow rates and adjust them in real time to maintain the desired mixing ratio. Sophisticated control algorithms can compensate for variations in fluid properties and external factors, such as temperature and pressure changes, which could otherwise affect the accuracy of the mixing process.
One of the challenges faced by Volumetric Ratio Mixers is the potential for wear and tear on the components, particularly the flow meters. Over time, the moving parts can become less accurate, causing deviations in the mixing ratio. Regular maintenance and replacement of these parts are crucial to preserving the mixer's precision. Additionally, the use of high-quality materials that are resistant to corrosion and wear can extend the life of the mixer and reduce the frequency of maintenance.
Another factor that can impact the precision of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer is the presence of air bubbles or entrained gases in the fluids. These can cause fluctuations in the measured flow rates, causing' inaccuracies in the mixing ratio. To mitigate this, some mixers incorporate degassing systems that remove gases from the fluids before they enter the mixing chamber.
The software that controls the Volumetric Ratio Mixer is also a critical component of the system. It must be capable of handling complex control algorithms and provide a user-friendly interface for operators to input the desired mixing ratios and monitor the process. Advanced software can also provide diagnostic tools that help identify and troubleshoot issues that could affect the precision of the mixer.
In conclusion, the precision of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer is a multifaceted issue that involves the careful design of the mixer, the calibration and maintenance of flow meters, the sophistication of the control systems, and the quality of the software that manages the process. By addressing these factors, industries can rely on Volumetric Ratio Mixers to deliver consistent and accurate mixing ratios, which is essential for the quality and safety of their products. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of Volumetric Ratio Mixers will only improve, further enhancing their role in precision mixing applications.
Recommended Products
-
Modol: Auto Loader-TMAL-300G
TMAL-300G Small Plastic Auto Loader Automatic Material Feeding Machine
 See More
See More 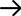
-
Modol: Multi-station-Hopper-Loaders-TMAL
High-Efficiency One-To-Many Hopper Suction Machines Can Be Equipped With 6 Hoppers
 See More
See More 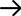
-
Modol: Plastic Auto Loader hopper
Multi-Style And Multi-Standard Adaptive Plastic Auto Loader Hopper
 See More
See More 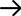
-
Modol: Standard Dehumidifier
Standard Intelligent Rotary Air Dehumidifier For Industrial Use
 See More
See More 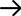


 English
English عربى
عربى




