Volumetric Ratio Mixers and Vertical Color Mixers in Diverse Working Conditions
Design Vertical Color Volumetric Ratio Mixer Manufacturer
In the intricate world of material processing, particularly within the plastics industry, the ability to blend and colorize raw materials effectively is paramount. The Volumetric Ratio Mixer and the Vertical Color Mixer is two types of equipment that have been designed to cater to these needs. Their applicability, however, can vary significantly depending on the specific working conditions, including the type of plastic granules being processed and the color requirements of the end product. This article aims to explore the suitability of Volumetric Ratio Mixers and Vertical Color Mixers under different operational scenarios.
Volumetric Ratio Mixers are engineered to blend materials based on a precise volume ratio, ensuring that the components are mixed uniformly. This precision is particularly beneficial when dealing with plastic granules that require a consistent blend to meet stringent quality standards. The applicability of Volumetric Ratio Mixers is heightened in environments where the plastic granules have similar densities and flow characteristics, as these factors can influence the accuracy of the volume-based mixing process.
On the other hand, Vertical Color Mixers are specifically designed to achieve a uniform color distribution within the plastic material. These mixers are equipped with features that promote mixing, such as high-speed rotation and specialized blades that can break up and disperse color concentrates effectively. The suitability of Vertical Color Mixers is often determined by the complexity of the color requirements. For instance, when dealing with intricate color patterns or when a high degree of color uniformity is necessary, Vertical Color Mixers prove to be invaluable.
The type of plastic granules being processed also plays a crucial role in determining the applicability of these mixers. Volumetric Ratio Mixers are more suitable for granules with similar physical properties, as they rely on volume to achieve a balanced mix. In contrast, Vertical Color Mixers can handle a wider range of granule types, as their design focuses on ensuring color uniformity rather than the physical properties of the materials being mixed.
Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can also impact the performance of these mixers. Volumetric Ratio Mixers may require a controlled environment to maintain the accuracy of the volume measurements, especially when dealing with materials that are sensitive to temperature changes. Vertical Color Mixers, while also affected by environmental conditions, are generally more robust and can operate effectively in a broader range of settings.
Moreover, the scale of operation is another factor to consider when assessing the applicability of Volumetric Ratio Mixers and Vertical Color Mixers. Volumetric Ratio Mixers are often more suitable for smaller-scale operations where precision is key, while Vertical Color Mixers can be adapted to both small and large-scale processes, depending on the design and capacity of the mixer.
In conclusion, the applicability of Volumetric Ratio Mixers and Vertical Color Mixers is influenced by a multitude of factors, including the type of plastic granules, color requirements, environmental conditions, and the scale of operation. Volumetric Ratio Mixers excel in scenarios where precise volume-based mixing is crucial, particularly with granules of similar properties. Vertical Color Mixers, with their focus on achieving color uniformity, are versatile and can be adapted to a wide range of applications, from intricate color patterns to large-scale production needs. By understanding the unique strengths and limitations of each mixer type, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their material processing and colorization processes.
Recommended Products
-
Modol: Auto Loader-TMAL-300G
TMAL-300G Small Plastic Auto Loader Automatic Material Feeding Machine
 See More
See More 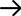
-
Modol: Multi-station-Hopper-Loaders-TMAL
High-Efficiency One-To-Many Hopper Suction Machines Can Be Equipped With 6 Hoppers
 See More
See More 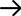
-
Modol: Plastic Auto Loader hopper
Multi-Style And Multi-Standard Adaptive Plastic Auto Loader Hopper
 See More
See More 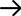
-
Modol: Standard Dehumidifier
Standard Intelligent Rotary Air Dehumidifier For Industrial Use
 See More
See More 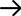


 English
English عربى
عربى




