Assessing the Homogeneity of Mixtures with Volumetric Ratio Mixers
Sale Color Paint Volumetric Ratio Mixer Machine Company
The homogeneity of a mixture is a critical parameter in industries where precise blending is essential for product quality and consistency. The Volumetric Ratio Mixer is widely used in these contexts due to its ability to blend components in a controlled and accurate manner. However, assessing the homogeneity of the mixtures produced by these Volumetric Ratio Mixers is a complex task that requires a multifaceted approach.
The homogeneity of a mixture produced by a Volumetric Ratio Mixer can be evaluated through various methods, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. One common method is to use sampling techniques, where small samples of the mixture are taken at different points within the mixing vessel and analyzed for uniformity. This method relies on the assumption that the samples are representative of the entire mixture, which can be a challenge in large-scale industrial applications.
Another approach to assessing the homogeneity of mixtures produced by Volumetric Ratio Mixers is through the use of in-line sensors. These sensors can provide real-time data on the composition of the mixture as it is being blended, allowing for immediate adjustments to be made if the desired ratio is not being achieved. However, the accuracy of these sensors can be influenced by factors such as the viscosity of the components being mixed and the presence of any contaminants.
In addition to these direct methods of assessing homogeneity, there are also indirect methods that can provide valuable insights. For example, the energy consumption of the Volumetric Ratio Mixer can be monitored, as higher energy usage may indicate that the Volumetric Ratio Mixer is working harder to achieve a uniform blend. Similarly, the temperature of the mixture can be tracked, as uneven heating can cause variations in the properties of the components being mixed.
The design of the Volumetric Ratio Mixer itself can also impact the homogeneity of the mixture. Features such as the shape and size of the mixing vessel, the type and configuration of the mixing blades, and the speed and direction of rotation can all influence the efficiency with which the components are blended. Engineers must carefully consider these factors when designing a Volumetric Ratio Mixer to ensure that it can achieve the desired level of homogeneity.
Furthermore, the properties of the components being mixed can also affect the homogeneity of the mixture. For example, components with different densities or viscosities may require different mixing techniques to ensure that they are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. In some cases, additional steps such as pre-mixing or the use of surfactants may be necessary to achieve the desired level of homogeneity.
In conclusion, assessing the homogeneity of mixtures produced by Volumetric Ratio Mixers is a complex task that requires a combination of direct and indirect methods. By carefully considering factors such as the design of the Volumetric Ratio Mixer, the properties of the components being mixed, and the use of in-line sensors and sampling techniques, it is possible to evaluate the homogeneity of the mixture and make any necessary adjustments to the mixing process. This attention to detail is essential for ensuring that the final product meets the required specifications and maintains possible quality.
Recommended Products
-
Modol: Auto Loader-TMAL-300G
TMAL-300G Small Plastic Auto Loader Automatic Material Feeding Machine
 See More
See More 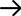
-
Modol: Multi-station-Hopper-Loaders-TMAL
High-Efficiency One-To-Many Hopper Suction Machines Can Be Equipped With 6 Hoppers
 See More
See More 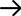
-
Modol: Plastic Auto Loader hopper
Multi-Style And Multi-Standard Adaptive Plastic Auto Loader Hopper
 See More
See More 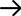
-
Modol: Standard Dehumidifier
Standard Intelligent Rotary Air Dehumidifier For Industrial Use
 See More
See More 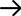


 English
English عربى
عربى




