Investigating the Energy Consumption of Volumetric Ratio Mixers
Design Color Paint Volumetric Ratio Mixer Machine Factory
In the quest for sustainable industrial practices, the energy consumption of equipment such as the Volumetric Ratio Mixer has become a significant area of focus. These mixers are integral to many manufacturing processes, where precise blending of components is essential. The efficiency of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer is not only measured by its ability to achieve the desired mixing ratio but also by how it performs this task with energy expenditure.
The energy consumption of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer is influenced by several factors, including the design of the mixer, the materials being mixed, and the operational parameters such as speed and duration of the mixing process. Advanced Volumetric Ratio Mixers are engineered to decrease energy use while maintaining high standards of mixing efficiency. This is achieved through the use of high-quality materials that reduce friction, the implementation of energy-saving motors, and the incorporation of smart control systems that optimize the mixing process.
One of how Volumetric Ratio Mixers reduce energy consumption is through their design. A well-designed mixer will have a more efficient impeller system that can achieve the desired mixing action with less power. This is particularly important in large-scale industrial applications where the mixers are in operation for extended periods. The use of materials with low friction coefficients, such as certain types of stainless steel or specialized coatings, can also contribute to reduced energy consumption.
Another aspect of energy efficiency in Volumetric Ratio Mixers is the control system. Modern mixers are often equipped with advanced control systems that monitor and adjust the mixing process in real time. These systems can optimize the speed and duration of the mixing process to achieve the desired outcome with an amount of energy. By precisely controlling the operational parameters, the mixer can avoid unnecessary energy use that would occur if it were running at a constant speed or for longer than necessary.
The materials being mixed also play a role in the energy consumption of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer. Some materials are more challenging to mix than others, requiring more energy to achieve a homogeneous blend. In such cases, the mixer may need to work harder, which can cause increased energy use. However, by carefully selecting the appropriate mixer for the specific materials being processed, it is possible to decrease this impact.
Furthermore, the operational parameters of a Volumetric Ratio Mixer can be adjusted to optimize energy consumption. For example, the speed at which the mixer operates can be fine-tuned to ensure that the materials are thoroughly mixed without wasting energy. Similarly, the duration of the mixing process can be optimized to ensure that the materials are fully blended without overmixing, which can also consume unnecessary energy.
In conclusion, the energy consumption of Volumetric Ratio Mixers is a complex issue that involves a variety of factors. By focusing on the design of the mixer, the materials being mixed, and the operational parameters, it is possible to optimize the energy efficiency of these mixers. This not only contributes to more sustainable industrial practices but also can cause cost savings for the companies that use these mixers. As technology continues to advance, the energy consumption of Volumetric Ratio Mixers will likely continue to decrease, making them an even more attractive option for industries that require precise mixing of components.
Recommended Products
-
Modol: Auto Loader-TMAL-300G
TMAL-300G Small Plastic Auto Loader Automatic Material Feeding Machine
 See More
See More 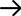
-
Modol: Multi-station-Hopper-Loaders-TMAL
High-Efficiency One-To-Many Hopper Suction Machines Can Be Equipped With 6 Hoppers
 See More
See More 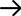
-
Modol: Plastic Auto Loader hopper
Multi-Style And Multi-Standard Adaptive Plastic Auto Loader Hopper
 See More
See More 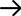
-
Modol: Standard Dehumidifier
Standard Intelligent Rotary Air Dehumidifier For Industrial Use
 See More
See More 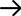


 English
English عربى
عربى




